Obesity in Cats: Understanding the Risks and How to Prevent It
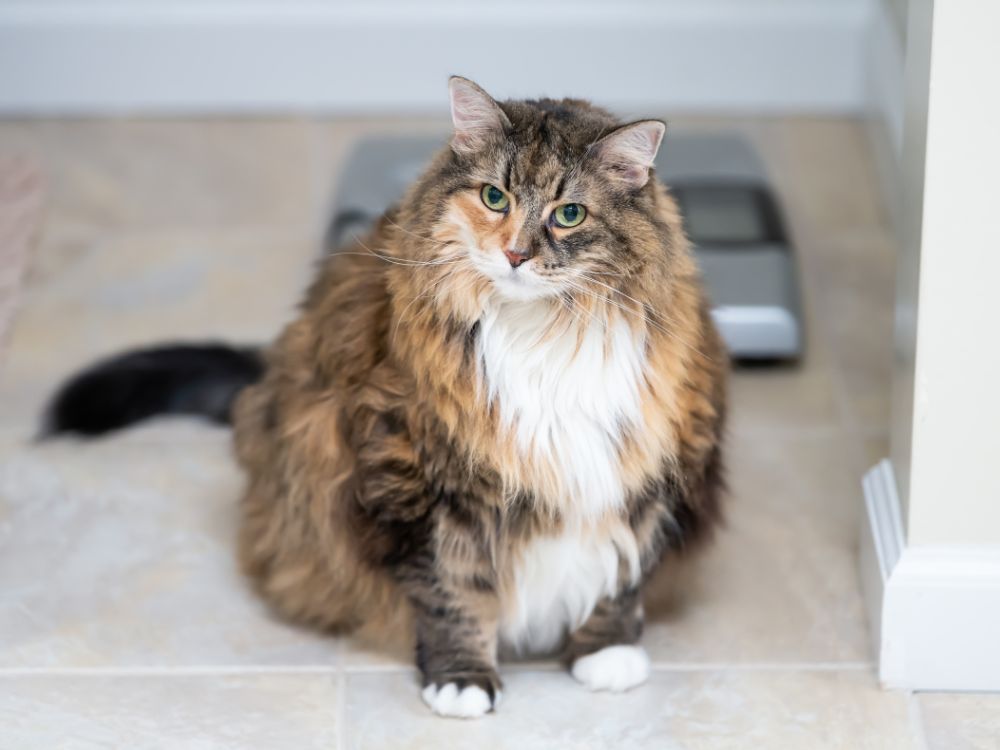

Obesity in cats is a growing concern among pet owners and veterinarians alike. As our feline friends increasingly lead more sedentary lifestyles and consume calorie-rich diets, the risk of obesity rises. Understanding the dangers of obesity and how to prevent it is crucial for any cat owner who wants to ensure their pet lives a long, healthy life.
Understanding Obesity in Cats
Obesity occurs when a cat consumes more calories than it burns off through physical activity, leading to an accumulation of excess body fat. This condition can affect cats of all breeds and ages, but it’s particularly common in indoor cats. An obese cat often struggles with mobility, tires easily, and may show signs of discomfort when moving.
The Dangers of Cat Obesity
The dangers of obesity in cats extend far beyond a few extra pounds. Obese cats are at a higher risk for several serious health conditions, many of which can significantly reduce their lifespan and quality of life.
1. Diabetes Mellitus
Obesity is a leading cause of diabetes mellitus in cats. Excess body fat affects the way a cat’s body responds to insulin, leading to insulin resistance. This condition requires lifelong management, including daily insulin injections and strict dietary control.
2. Joint and Mobility Issues
Carrying excess weight puts additional strain on a cat’s joints, particularly the hips and knees. Over time, this can lead to arthritis, a painful condition that makes movement difficult and uncomfortable. An obese cat is less likely to engage in physical activity, further worsening the condition.
3. Cardiovascular Problems
An overweight cat faces a higher risk of developing heart disease. The heart has to work harder to pump blood through the body, which can lead to an enlarged heart, high blood pressure, and other cardiovascular issues. These conditions can be life-threatening if not managed properly.
4. Liver Disease
Obesity can lead to hepatic lipidosis, also known as fatty liver disease. This condition occurs when excess fat is stored in the liver, impairing its function. Without treatment, hepatic lipidosis can be fatal.
5. Respiratory Problems
Excess fat around the chest and abdomen can make it difficult for an obese cat to breathe properly. This can lead to shortness of breath, increased respiratory effort, and in severe cases, respiratory failure.
6. Reduced Lifespan
The combined effects of these health issues can significantly shorten the lifespan of an obese cat. Studies have shown that overweight cats are more likely to die prematurely compared to cats of a healthy weight.
Preventing Obesity in Cats
Preventing obesity in cats requires a combination of proper diet, regular exercise, and routine veterinary care. By taking proactive steps, you can help your cat maintain a healthy weight and avoid the dangers associated with obesity.
1. Monitor Your Cat’s Diet
The first step in preventing obesity is controlling your cat’s diet. Feed your cat a balanced, portion-controlled diet that meets their nutritional needs without providing excess calories. Choose high-quality cat food that is appropriate for your cat’s age, breed, and activity level. Avoid free-feeding or leaving food out all day, as this can lead to overeating.
2. Encourage Physical Activity
Regular exercise is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight in cats. Encourage your cat to stay active by providing toys, climbing structures, and interactive play sessions. Laser pointers, feather wands, and puzzle toys can stimulate your cat’s natural hunting instincts and keep them moving. Aim for at least 20-30 minutes of active playtime each day.
3. Schedule Regular Vet Visits
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for monitoring your cat’s weight and overall health. Your veterinarian can assess your cat’s body condition, provide dietary recommendations, and identify any underlying health issues that may contribute to weight gain. Early detection of weight-related problems can prevent more serious health issues down the line.
4. Consider a Weight Management Program
If your cat is already overweight, consider enrolling them in a weight management program. Many veterinary clinics offer programs tailored to help obese cats lose weight safely and effectively. These programs typically include a customized diet plan, regular weigh-ins, and guidance on increasing physical activity.
5. Avoid Overfeeding and Treats
It’s easy to overfeed your cat, especially if you’re in the habit of giving them treats or table scraps. Treats should make up no more than 10% of your cat’s daily caloric intake. Opt for low-calorie treats or use small portions of your cat’s regular food as treats. Avoid feeding human food, as it often contains ingredients that are harmful or fattening for cats.
6. Monitor Weight and Body Condition
Regularly monitoring your cat’s weight and body condition can help you catch weight gain early. Feel for your cat’s ribs and observe their waistline—both should be easily noticeable without excess fat. If you notice any changes in your cat’s body condition, adjust their diet and exercise routine accordingly.
Conclusion: Taking Action Against Obesity in Cats
Preventing obesity in cats requires diligence and a commitment to your cat’s health. By understanding the risks associated with obesity and taking proactive steps, you can help your cat maintain a healthy weight and avoid the dangers of obesity. Remember, a healthy cat is a happy cat, and by keeping your feline friend fit and active, you’ll ensure they enjoy a long, fulfilling life.
For more tips and insights on maintaining your cat’s health, be sure to check out our Health and Care category. Here, you’ll find a wealth of information on various topics related to your cat’s well-being.